11/02/2024
Types of Carbon Emissions: A Guide to Scope 1, 2, and 3
Understanding the different types of carbon emissions is crucial. Luckily, they’re categorized into three different scopes.

9 February 2024
Discover the essentials of carbon accounting, a key strategy in the fight against climate change. Learn about its impact, methodologies, and the future of sustainable practices in our concise guide.
Today, in our eco-friendly world, carbon accounting is a vital tool to address climate change.
But what exactly is carbon accounting?
Carbon accounting, or greenhouse gas accounting, is the process of measuring and tracking the amount of carbon dioxide emissions produced by an organization, individual, product, or event. This essential practice serves as the foundation for informed decision-making on reducing carbon footprints and mitigating climate impact.
As people globally work towards achieving net-zero emissions, they are also demanding greater transparency in environmental responsibility. In this context, the carbon account plays a crucial role. Carbon accounting plays a crucial role in assisting businesses and governments to meet global climate goals, such as the EU Green Deal and the Paris Agreement.
It is vital for enabling businesses not only to meet these climate goals but also to stay compliant with carbon reporting legislation, and build brand equity. Additionally, carbon accounting aids consumers in making more environmentally friendly choices, underscoring its importance across various sectors
By quantifying emissions, carbon accounting provides a clear pathway for implementing effective carbon management strategies and sustainability practices.
Moreover, in an era where environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria are becoming critical in investment decisions. Carbon accounting stands out as a vital component influencing ESG reporting and investment. It provides a quantifiable measure of a company’s environmental impact, which improves its reputation and market competitiveness.
Let’s break down the basics of carbon accounting, exploring its key principles and operational mechanisms. Let’s go through the structured steps that make carbon accounting an indispensable tool in the fight against climate change.
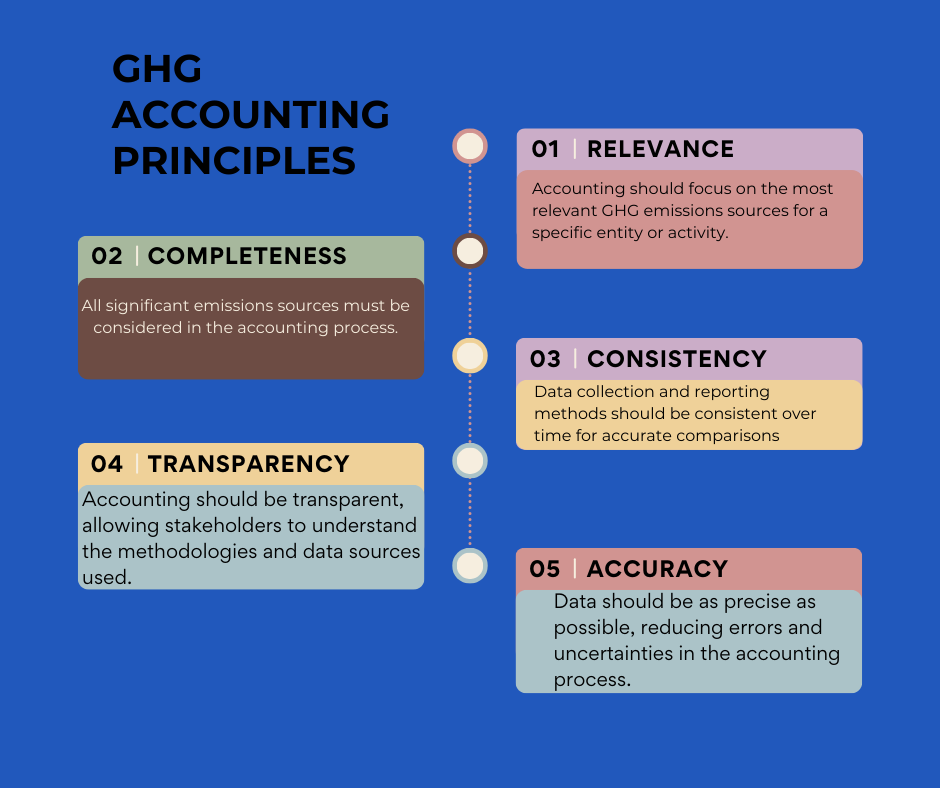
Carbon accounting operates on a set of guiding principles designed to ensure accuracy, transparency, and consistency in measuring and reporting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. These fundamental principles include:
The carbon accounting method is tailored to match the entity’s specific needs and goals, ensuring that the data obtained is directly applicable to the entity’s sustainability objectives.
Capturing all relevant emission sources within the defined scope, providing a comprehensive view of an entity’s carbon footprint.
To ensure accurate comparisons, it’s important that methods of gathering and reporting data remain consistent throughout the period of observation.
Maintaining open and clear documentation of all carbon accounting processes, methodologies, and results to build trust and credibility.
Striving for precision in emissions measurement to ensure reliable and verifiable data.
Setting off on the carbon accounting journey reveals a thorough process that is critical for enterprises committed to sustainability.
The task begins by mapping the area and establishing the scope of emissions to be included.The first step is to separate emissions into three categories or scopes: scope 1, scope 2, and scope 3.
After the scope is defined, the search for data begins. This phase involves a deep dive into gathering information on every relevant emission source.
A task that requires both precision and collaboration. Accessing internal records and engaging with suppliers or partners are key in assembling the emission sources. This phase requires careful work because the accuracy of carbon accounting depends on how complete and reliable the collected data is.
At the core of carbon accounting is the calculation phase, where data transforms into insights. Using standardized emissions factors, organizations translate their activities into carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e), the universal metric for measuring greenhouse gas emissions.
These factors, based on credible sources like the EPA, the IEA, or Ademe (base empreinte), act as the standards for measuring the environmental impact of various activities, from using energy to transportation.
After gathering all the needed information, including company data and emission factors, the company is ready to carry out its carbon accounting.
The process now shifts towards being open and checked thoroughly. Emissions that have been calculated are verified to make sure the data is accurate and reliable. This involves checks, either by the company itself or by outsiders, to ensure everything is correct and trustworthy. This step helps to build confidence.
Afterwards, the data should be shared to stakeholders, including employees, investors, and regulators. This enhances transparency and allows companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability goals.
Understanding these principles and steps is essential for anyone looking to effectively implement carbon accounting within their company. By embracing these fundamental principles, organizations can not only assess their environmental impact but also identify potential opportunities for significant carbon reductions. If you want to learn more about these principles you can read the GHG Protocol Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard here.
Carbon accounting has never been more relevant or urgent in the ever-changing context of environmental sustainability. It is a critical approach for organizations looking for ways to resolve the problems of climate change, fulfill global climate targets, and improve operational transparency and efficiency.
Pilario brings together carbon accounting and LCA (Life Cycle Assessment) in a powerful way, making it super useful for businesses looking to reduce and assess their environmental impact. With carbon accounting, you can keep track of your greenhouse gas emissions. LCA gives you the bigger picture, showing how your products affect the environment from start to finish. Pilario makes it easy to find out where you need to make changes, helping you improve not just your carbon footprint but all kinds of environmental impacts.

11/02/2024
Understanding the different types of carbon emissions is crucial. Luckily, they’re categorized into three different scopes.

22/09/2023
Unlock sustainable success with LCA, PEF, and PEFCR. Understand environmental impacts, gain trust, and comply with EU standards effortlessly.

11/02/2024
Organizations need guidelines to measure, report, and reduce their greenhouse gas emissions when implementing carbon accounting.

11/02/2024
Explore the future of carbon accounting as we tackle current challenges and predict digital innovations. Dive into our guide.